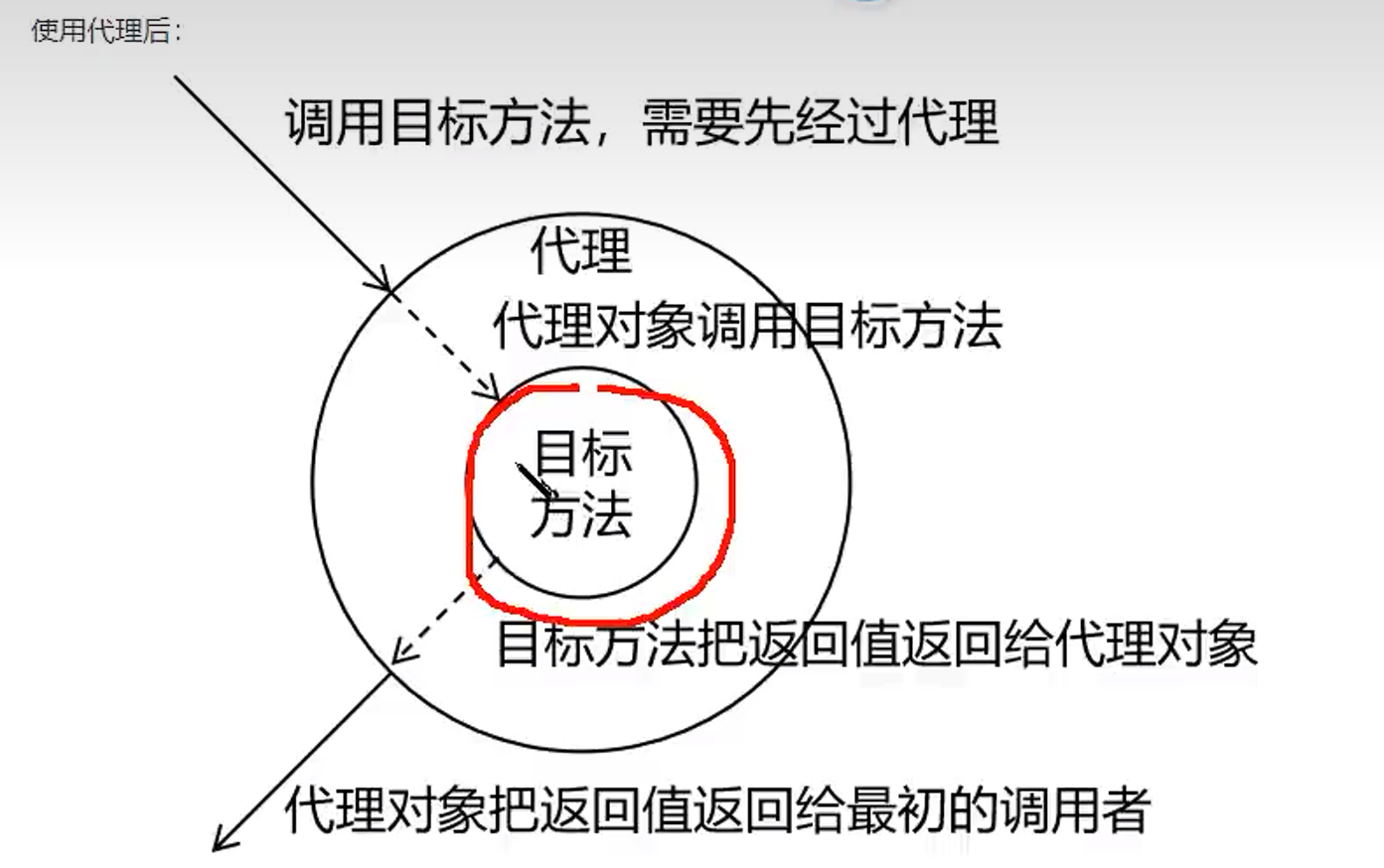
AOP的使用
还是重新看一遍这个吧,现在是完全不会好吧
注解实现AOP
首先是applicationContext.xml配置文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:app="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.zzmr.aop.annotation"/>
<app:aspectj-autoproxy/>
</beans>
|
主要就是那一行<app:aspectj-autoproxy/>
接口:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| package com.zzmr.aop.annotation;
public interface Calculator {
int add(int i, int j);
int sub(int i, int j);
int mul(int i, int j);
int div(int i, int j);
}
|
接口实现类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| package com.zzmr.aop.annotation;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class CalculatorImpl implements Calculator {
@Override
public int add(int i, int j) {
int result = i + j;
System.out.println("方法内部:result:" + result);
return result;
}
@Override
public int sub(int i, int j) {
int result = i - j;
System.out.println("方法内部:result:" + result);
return result;
}
@Override
public int mul(int i, int j) {
int result = i * j;
System.out.println("方法内部:result:" + result);
return result;
}
@Override
public int div(int i, int j) {
int result = i / j;
System.out.println("方法内部:result:" + result);
return result;
}
}
|
切面类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
| package com.zzmr.aop.annotation;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
@Aspect
@Component
public class LoggerAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.zzmr.aop.annotation.CalculatorImpl.*(..))")
public void pointCut() {
}
@Before("pointCut()")
public void beforeAdviceMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
System.out.println("LoggerAspect:前置通知" + "方法:" + signature.getName() + " 参数:" + Arrays.toString(args));
}
@After("pointCut()")
public void afterAdviceMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
System.out.println("LoggerAspect:后置通知" + "方法:" + signature.getName() + " 参数:" + Arrays.toString(args));
}
@AfterReturning(value = "pointCut()", returning = "result")
public void afterReturningAdviceMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("LoggerAspect:返回通知" + "方法:" + signature.getName() + ",结果:" + result);
}
@AfterThrowing(value = "pointCut()", throwing = "ex")
public void afterThrowingAdviceMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable ex) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("LoggerAspect:异常通知" + "方法:" + signature.getName() + "异常:" + ex);
}
@Around(value = "pointCut()")
public Object aroundAdviceMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {
Object result = null;
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
try {
System.out.println("环绕通知:前置通知的位置" + "参数:" + Arrays.toString(args));
result = joinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("环绕通知:返回通知的位置" + "结果:" + result);
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("环绕通知:异常通知的位置" + "异常为:" + e);
} finally {
System.out.println("环绕通知:后置通知的位置");
}
return result;
}
}
|
测试代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| package com.zzmr.aop.annotation;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class AspectTest {
@Test
public void testBean() {
ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Calculator calculator = ioc.getBean(Calculator.class);
int result1 = calculator.div(4, 3);
}
}
|
注意事项
添加代理对象之后,不能直接获取目标对象了,而是要使用目标对象的接口(代理对象)来获取
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| @Test
public void testBefore(){
ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("aop-annotation.xml");
Calculator calculator = ioc.getBean(Calculator.class);
int result = calculator.add(1, 1);
}
|
重用切入点表达式,使用@PointCut()注解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
@Pointcut("execution(* com.zzmr.aop.annotation.CalculatorImpl.*(..))")
public void pointCut() {
}
|
JoinPoint和signature以及args
- JoinPoint:连接点,可以获取签名信息:
joinPoint.getSignature()
- signature:签名信息,可以通过它获取方法名
signature.getName()
- args:参数列表,通过joinPoint.getArgs()获取
每个通知方法的参数有joinPoint和result,result就是方法的返回值
环绕通知比较特殊,是一个通知包含了所有其他的通知:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| @Around(value = "pointCut()")
public Object aroundAdviceMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {
Object result = null;
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
try {
System.out.println("环绕通知:前置通知的位置" + "参数:" + Arrays.toString(args));
result = joinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("环绕通知:返回通知的位置" + "结果:" + result);
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("环绕通知:异常通知的位置" + "异常为:" + e);
} finally {
System.out.println("环绕通知:后置通知的位置");
}
return result;
}
|
其中的joinPoint.proceed()就表示方法执行
没想到有一天我还会更新这篇文章
主要是写苍穹外卖的时候,用到了AOP
话不多说,上代码
自定义注解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| package com.zzmr.osstest.annoatation;
import com.zzmr.osstest.enumeration.OperationType;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface AutoInsert {
OperationType value();
}
|
枚举类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| package com.zzmr.osstest.enumeration;
public enum OperationType {
ADD,
SUB,
MUL,
DIV
}
|
切面类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
| package com.zzmr.osstest.aspect;
import com.zzmr.osstest.annoatation.AutoInsert;
import com.zzmr.osstest.enumeration.OperationType;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
@Aspect
@Component
@Slf4j
public class AutoInsertAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.zzmr.osstest.testaspect.*.*(..)) && @annotation(com.zzmr.osstest.annoatation" +
".AutoInsert)")
public void autoInsertPointcut() {
}
@Before("autoInsertPointcut()")
public void autoInsert(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
AutoInsert annotation = methodSignature.getMethod().getAnnotation(AutoInsert.class);
OperationType type = annotation.value();
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
try {
Method setA = args[0].getClass().getDeclaredMethod("setA", int.class);
Method setB = args[0].getClass().getDeclaredMethod("setB", int.class);
if (type == OperationType.ADD) {
setA.invoke(args[0], 50);
setB.invoke(args[0], 60);
log.info("是加的操作,结果应为110");
} else if (type == OperationType.SUB) {
setA.invoke(args[0], 100);
setB.invoke(args[0], 70);
log.info("是减的操作,结果应为30");
} else if (type == OperationType.MUL) {
setA.invoke(args[0], 3);
setB.invoke(args[0], 4);
log.info("是乘的操作,结果应为12");
} else if (type == OperationType.DIV) {
setA.invoke(args[0], 36);
setB.invoke(args[0], 2);
log.info("是除的操作,结果应为18");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
实体类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| package com.zzmr.osstest.model;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import lombok.ToString;
@Data
@ToString
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class NumberTest {
public int a = 10;
public int b = 20;
}
|
用于测试的接口和实现类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
| package com.zzmr.osstest.testaspect;
import com.zzmr.osstest.model.NumberTest;
public interface CalTest {
void add(NumberTest numberTest);
void div(NumberTest numberTest);
void sub(NumberTest numberTest);
void mul(NumberTest numberTest);
}
package com.zzmr.osstest.testaspect;
import com.zzmr.osstest.annoatation.AutoInsert;
import com.zzmr.osstest.enumeration.OperationType;
import com.zzmr.osstest.model.NumberTest;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class CalTestImpl implements CalTest {
@Override
@AutoInsert(value = OperationType.ADD)
public void add(NumberTest numberTest) {
int num1 = numberTest.getA();
int num2 = numberTest.getB();
log.info("开始add");
log.info("结果: {}", num1 + num2);
}
@AutoInsert(value = OperationType.DIV)
@Override
public void div(NumberTest numberTest) {
int num1 = numberTest.getA();
int num2 = numberTest.getB();
log.info("开始div");
log.info("结果: {}", num1 / num2);
}
@AutoInsert(value = OperationType.SUB)
@Override
public void sub(NumberTest numberTest) {
int num1 = numberTest.getA();
int num2 = numberTest.getB();
log.info("开始sub");
log.info("结果: {}", num1 - num2);
}
@Override
@AutoInsert(value = OperationType.MUL)
public void mul(NumberTest numberTest) {
int num1 = numberTest.getA();
int num2 = numberTest.getB();
log.info("开始mul");
log.info("结果: {}", num1 * num2);
}
}
|
测试类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| package com.zzmr.osstest;
import com.zzmr.osstest.model.NumberTest;
import com.zzmr.osstest.testaspect.CalTest;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
public class StaticTest {
@Autowired
private CalTest calTest;
@Test
public void testAspect() {
NumberTest numberTest = new NumberTest();
numberTest.setA(10);
numberTest.setB(20);
calTest.add(numberTest);
System.out.println("=======================");
calTest.sub(numberTest);
System.out.println("=======================");
calTest.mul(numberTest);
System.out.println("=======================");
calTest.div(numberTest);
}
}
|
想说明什么呢
- 自定义注解的编写形式是固定的,要在类上方加上那两个注解
- 自定义注解中的枚举,
OperationType value();这段代码的意思就是这个注解的value属性可以有OperationType中的所有类型,当然,这个value名称也是自定义的
- 通过反射获取类中的方法:
Method setB = args[0].getClass().getDeclaredMethod("setB", int.class);,参数中第一个为方法名,第二个为该方法接受的参数类型
- 最后通过
invoke来调用方法:setB.invoke(args[0], 60);
这样对于使用AOP也算有了一点印象了..
2023年8月30日 13点45分